Coarsening for Algebraic Multigrid: Aggregation
Given a SPD matrix A, we describe an algebraic coarsening of a graph of A based on the concept of strong connectness and aggregation.
Contents
Usage of the function
clear all help coarsenAMGa
Parameters
Generate a test matrix
[node,elem] = squaremesh([0,1,0,1],1/32);
[node,elem] = circlemesh(0,0,1,1/11); % [node,elem] = uniformrefine(node,elem); % load lakemesh % load bunny [A,M] = assemblematrix(node,elem); % A = M; % test mass matrix. No coarsening is needed.
- Min quality 0.8504 - Mean quality 0.9898 - Uniformity 2.94%
Parameters
theta = 0.025;
N = size(A,1);
N0 = min(sqrt(N),10); % number of the coarest nodes
Generate strong connectness matrix
D = spdiags(1./sqrt(diag(A)),0,N,N); Am = D*A*D; % normalize diagonal of A [im,jm,sm] = find(Am); idx = (-sm > theta); % delete weakly connect off-diagonal and diagonal As = sparse(im(idx),jm(idx),sm(idx),N,N); % matrix for strong connectness As = As + speye(N); % add diagonal As1 = spones(As); % graph of As As2 = triu(As1*As1,1); % edges of the graph corresponding to As^2
Compute degree of vertex
deg = full(transpose(sum(As1))); % number of strongly connected neighbors if sum(deg>0) < 0.1*sqrt(N) % too few connected nodes e.g. A is mass matrix isC(round(rand(N0,1)*N)) = true; % randomly chose N0 nodes return % smoother is a good preconditioner end idx = (deg>0); deg(idx) = deg(idx) + 0.1*rand(sum(idx),1); % break the equal degree case
Find an approximate maximal independent set and put to C set
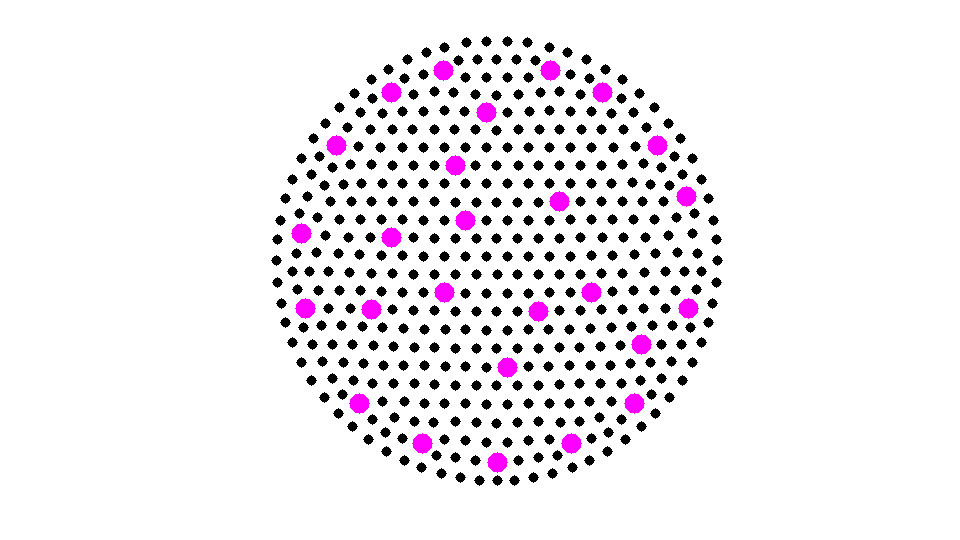
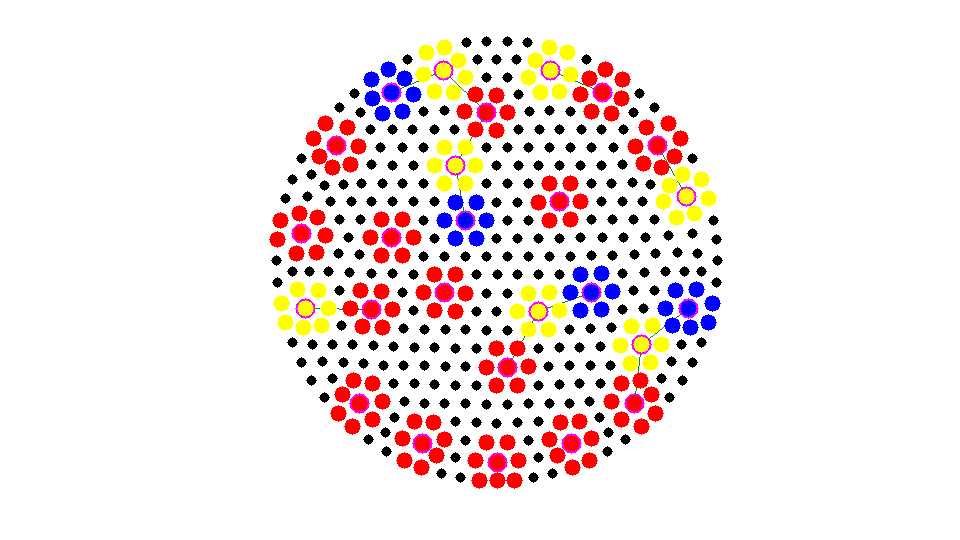
isC = false(N,1); % C: coarse node isF = false(N,1); % F: fine node isU = true(N,1); isS = true(N,1); % S: selected set isF(deg == 0) = true; % isolated nodes are added into F set % debug close all; % aggregrate numbering and pointer aggN = 0; node2agg = zeros(N,1); agg2node = zeros(N,1); set(gcf,'Units','normal'); set(gcf,'Position',[0.5,0.5,0.5,0.5]); % showmesh(node,elem); findnode(node,isU,'noindex','Color','k','MarkerSize',32); axis equal; axis off; m = 1; while sum(isC) < N/2 && sum(isS) >N0 % Mark all undecided nodes isS = false(N,1); % S: selected set, changing in the coarsening isS(deg>0) = true; S = find(isS); % isS(S(2:2:end)) = false; % S = S(1:2:end); % debug fprintf('Coarsening ... \n'); % Find marked nodes with local maximum degree % showagg(node,deg); [i,j] = find(As2(S,S)); % i,j and i<j: edges of subgraph S idx = deg(S(i)) >= deg(S(j)); % compare degree of vertices isS(S(j(idx))) = false; % remove vertices with smaller degree isS(S(i(~idx))) = false; % showmesh(node,elem); findnode(node,isS,'noindex','Color','m','MarkerSize',60); fprintf('Number of chosen points: %6.0u\n',sum(isS)); snapnow % Add new agg isC(isS) = true; newC = find(isS); newAgg = aggN+(1:length(newC)); aggN = aggN + length(newC); node2agg(newC) = newAgg; agg2node(newAgg) = newC; % showagg(node,node2agg); % Remove coarse nodes and neighboring nodes from undecided set U = find(isU); [i,j] = find(As(isU,newC)); %#ok<*NASGU> use original connectivity isF(U(i)) = true; % neighbor of C nodes are F nodes isU = ~(isF | isC); % U: undecided set node2agg(U(i)) = node2agg(newC(j)); % add neighbors into the same aggregrate % update degree of U deg(newC) = 0; % remove new selected coarse grid nodes deg(U(i)) = 0; % remove neighbors of new selected coarse grid nodes U = find(isU); [i,j] = find(As(U,isF)); % find neighbor of fine nodes deg(U(i)) = 0; % remove neighbors of existing agg % plot figure(1); % showmesh(node,elem); % findnode(node,isU,'noindex','Color','k','MarkerSize',30); % findnode(node,isF,'noindex','Color','y','MarkerSize',48); % findnode(node,isC,'noindex','Color','r','MarkerSize',52); showagg(node,node2agg,agg2node,As); fprintf('Add neighboring nodes into exisitng aggregates. \n'); snapnow m = m + 1; end agg2node = agg2node(1:max(node2agg)); fprintf('Apply %2.0u times and Number of Coarse Nodes: %6.0u\n',m,sum(isC));
Coarsening ... Number of chosen points: 26
Add neighboring nodes into exisitng aggregates.
Coarsening ... Number of chosen points: 12
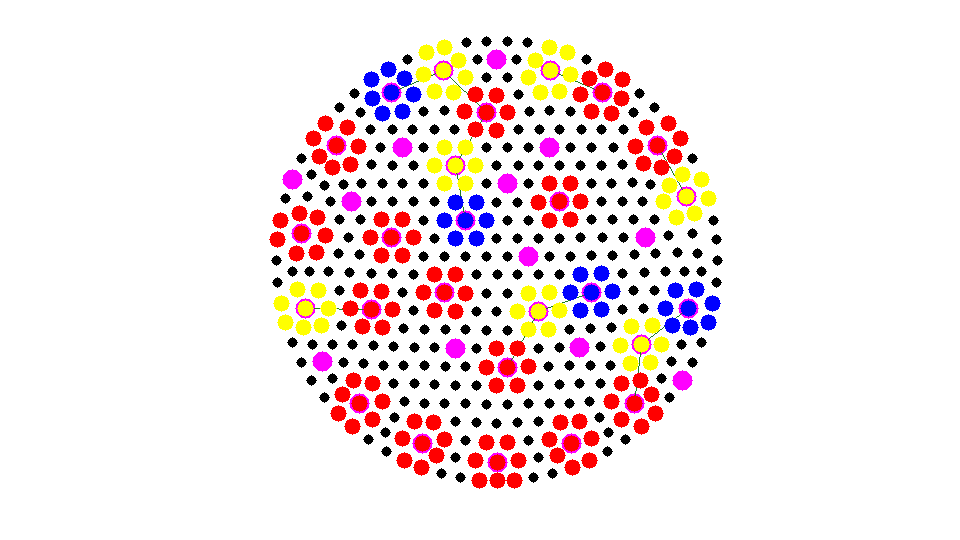
Add neighboring nodes into exisitng aggregates.
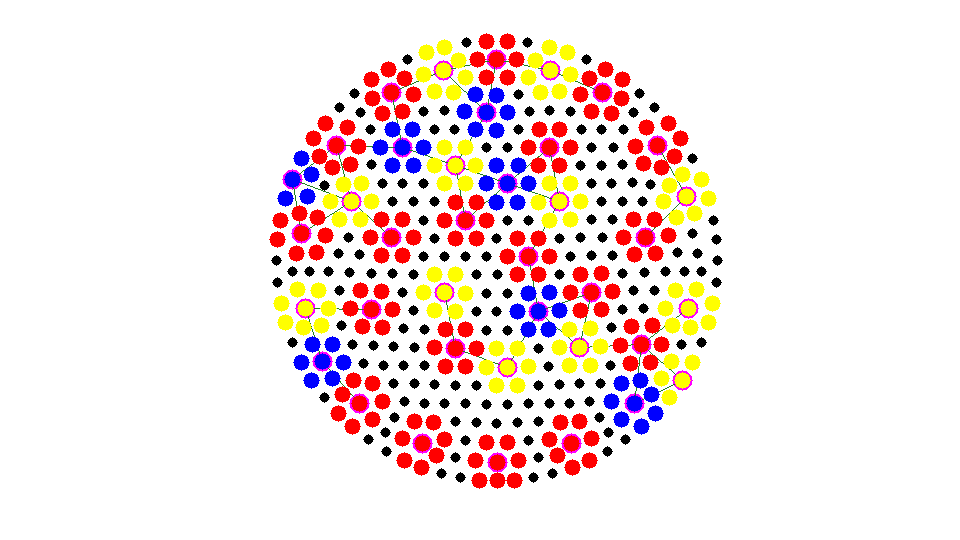
Coarsening ... Number of chosen points: 4

Add neighboring nodes into exisitng aggregates.
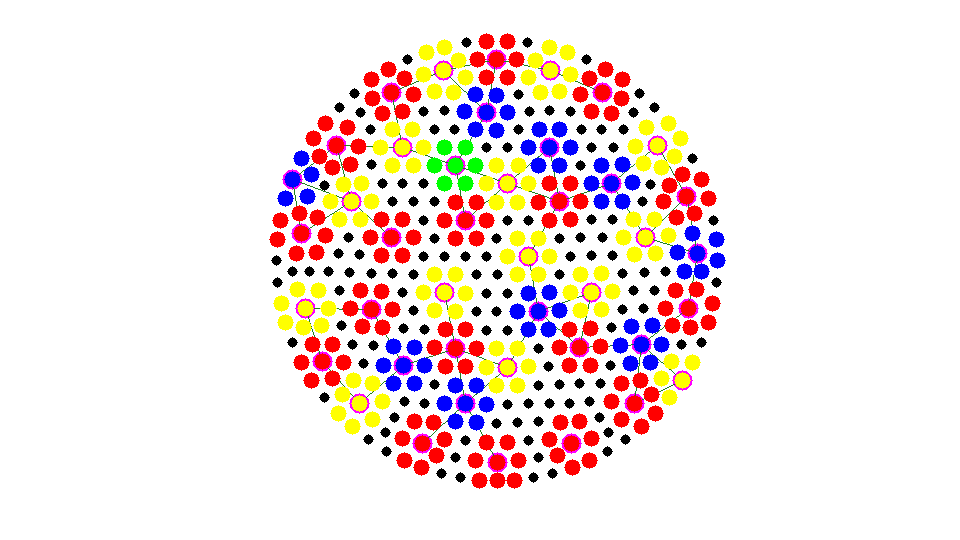
Apply 4 times and Number of Coarse Nodes: 42
Add left vertices to existing aggregate
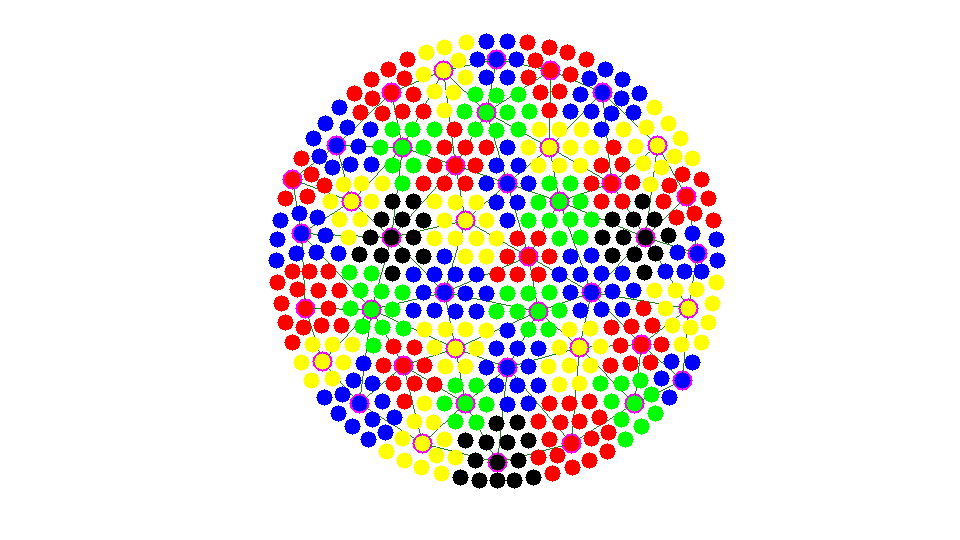
while any(isU) U = find(isU); [i,j] = find(As(:,isU)); %#ok<*NASGU> neighboring nodes of U % j: undecided vertices; i: neighbor of j neighborAgg = node2agg(i); % agg number of neighbors idx = (neighborAgg > 0); % a interior nodes could be left [nAgg,neighborAgg] = max(sparse(neighborAgg(idx),j(idx),1)); % a undecided node could be next to several aggregrates. find the one % with maximal neighboring aggregates. isbdU = (nAgg > 0); % find undecided nodes next to bdU = U(isbdU); % the boundary of aggregates node2agg(bdU) = neighborAgg(isbdU); % remove bdU from U and add to F isF(bdU) = true; isU(bdU) = false; % findnode(node,bdU,'noindex','Color','m'); showagg(node,node2agg,agg2node,As); fprintf('Add left nodes nodes to strongly connected aggregates.\n'); snapnow end
Add left nodes nodes to strongly connected aggregates.
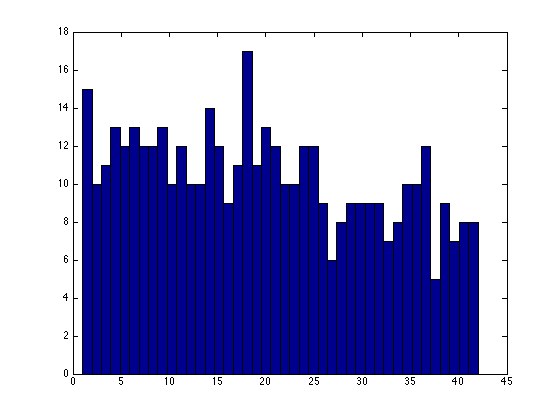
Check the number of nodes in aggregates
figure; hist(node2agg,max(node2agg));