CR Nonconforming P1 Element
We explain degree of freedoms for Crouzeix?Raviart nonconforming P1 element on triangles and tetrahedrons. The dofs are associated to edges (2-D) and faces (3-D). Given a mesh, the required data structure can be constructured by
[elem2edge,edge] = dofedge(elem); [elem2face,face] = dof3face(elem);
Contents
Local indexing of DOFs
node = [1,0; 1,1; 0,0]; elem = [1 2 3]; edge = [2 3; 1 3; 1 2]; figure(1); clf; set(gcf,'Units','normal'); set(gcf,'Position',[0,0,0.5,0.3]); subplot(1,2,1) showmesh(node,elem); findnode(node); findedge(node,edge); node = [0,0,0; 1,0,0; 0,1,0; 0,0,1]; elem = [1 2 3 4]; face = [2 3 4; 1 3 4; 1 2 4; 1 2 3]; subplot(1,2,2) showmesh3(node,elem); view([-26 10]); findnode3(node); findelem(node,face);

The three dofs associated to edges in a triangle is displayed in the left and the four dofs associated to faces of a tetrahedron is in the right. The dofs are indexed such that the i-th dof is opposite to the i-th vertex.
Local bases of CR element
The d+1 Lagrange-type bases functions are denoted by 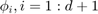 , i.e.
, i.e. 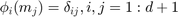 . In barycentric coordinates, they are:
. In barycentric coordinates, they are:
- 2-D:
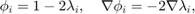
- 3-D:
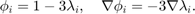
Global indexing of DOFs
node = [0,0; 1,0; 1,1; 0,1]; elem = [2,3,1; 4,1,3]; [node,elem] = uniformbisect(node,elem); figure(2); clf; showmesh(node,elem); findnode(node); findelem(node,elem); [elem2edge,edge] = dofedge(elem); findedge(node,edge);

The matrix elem2edge is the local to global index mapping of edges.
display(elem2edge);
elem2edge =
5 6 15
10 11 14
2 1 13
7 9 16
7 15 8
2 14 3
5 13 4
10 16 12