Mesh Smoothing and Optimization
Contents
Improve geometric mesh quality
The function [node,elem] = optmesh(node,elem) will optimize the shape regularity of triangles in the input mesh (node,elem) and outputs a better mesh (node,elem).
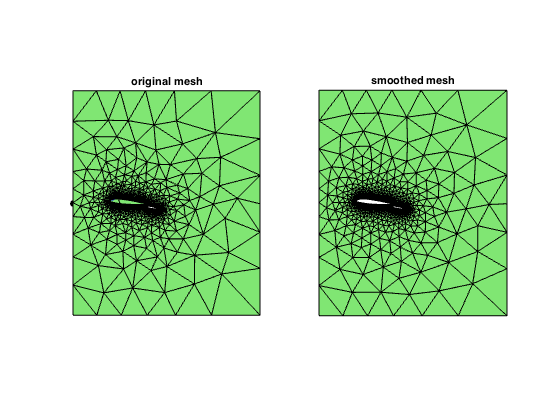
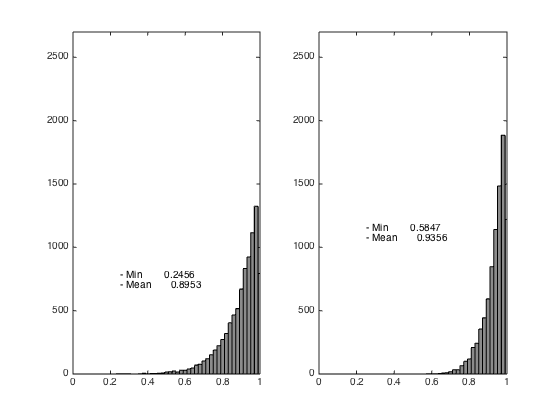
load airfoilperturbmesh figure(1); subplot(1,2,1); showmesh(node,elem); title('original mesh'); figure(2); subplot(1,2,1); showmeshquality(node,elem); axis([0 1 0 2700]); [node,elem] = optmesh(node,elem); figure(1); subplot(1,2,2); showmesh(node,elem); title('smoothed mesh'); figure(2); subplot(1,2,2); showmeshquality(node,elem); axis([0 1 0 2700]);
- Min quality 0.2456 - Mean quality 0.8953 Mesh quality before optimization - Min quality 0.2456 - Mean quality 0.8953 Mesh quality after optimization - Min quality 0.5847 - Mean quality 0.9356 - Min quality 0.5847 - Mean quality 0.9356
We explain algorithms implemented in optimesh.m in the following.
ODT-based mesh smoothing
In the function meshsmoothing, we move one node at a time inside its patch, which consists of all triangles surrounding this node, such that the interpolation error to a quadratic function is minimized. The function meshsmoothing will keep the topology of the input mesh, i.e., the node index and connectivity of nodes are unchanged.
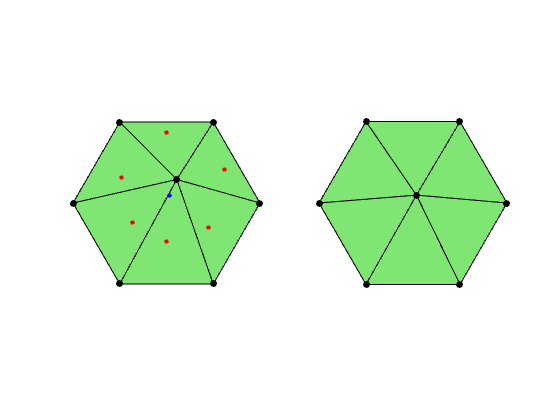
In the simplest case, the scheme is to move the node to the average of circumenters of triangles in the local patch. Details can be found in the paper ODTmesh.
theta = [-2*pi/3 -pi/3 0 pi/3 2*pi/3 pi]'; node = [cos(theta), sin(theta)]; node(end+1,:) = 0; elem = delaunayn(node); node(end,:) = rand(1,2)*0.4; figure(3); subplot(1,2,1); showmesh(node,elem); findnode(node,'all','noindex'); c = circumcenter(node,elem); hold on; plot(c(:,1),c(:,2),'r.','MarkerSize',16) node(end,:) = mean(c); plot(node(end,1),node(end,2),'b.','MarkerSize',16) figure(3); subplot(1,2,2); showmesh(node,elem); findnode(node,'all','noindex');