Contents
function [N,errL2,errH1,erruIuh] = squarePoisson
SQUAREPOISSON Poisson equation in a square domain.
squarePoisson computes approximations of the Poisson equation in the unit square on a sequence of meshes obtained by uniform refinement. It plots the approximation error (in L2 norm or H1 norm) vs the number of nodes.
See also Poisson, crack
% Copyright (C) Long Chen. See COPYRIGHT.txt for details. close all;
Parameters
maxIt = 7; N = zeros(maxIt,1); errL2 = zeros(maxIt,1); errH1 = zeros(maxIt,1); erruIuh = zeros(maxIt,1);
Generate an initial mesh
node = [0,0; 1,0; 1,1; 0,1]; % nodes elem = [2,3,1; 4,1,3]; % elements bdEdge = setboundary(node,elem,'Dirichlet','~(x==0)','Neumann','x==0'); % bdEdge = setboundary(node,elem,'Neumann'); [node,elem,bdEdge] = uniformrefine(node,elem,bdEdge); % [node,elem,bdEdge] = uniformbisect(node,elem,bdEdge);
Finite Element Method
for k = 1:maxIt [u,A] = Poisson(node,elem,bdEdge,@f,@g_D,[]); figure(1); showresult(node,elem,u); N(k) = size(elem,1); % compute error errL2(k) = computeL2error(node,elem,@exactu,u); errH1(k) = computeH1error(node,elem,@Du,u); uI = exactu(node); % nodal interpolation erruIuh(k) = sqrt((u-uI)'*A*(u-uI)); % refine grid [node,elem,bdEdge] = uniformrefine(node,elem,bdEdge); % [node,elem,bdEdge] = uniformbisect(node,elem,bdEdge); end
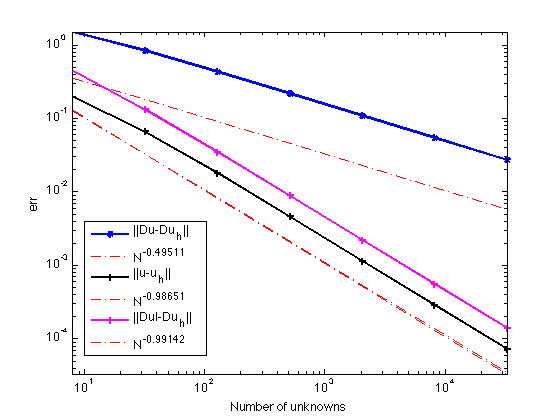
Plot convergence rates
figure(2); r1 = showrate(N,errH1,2,'-*'); hold on; r2 = showrate(N,errL2,2,'k-+'); r3 = showrate(N,erruIuh,2,'m-+'); legend('||Du-Du_h||',['N^{' num2str(r1) '}'], ... '||u-u_h||',['N^{' num2str(r2) '}'], ... '||DuI-Du_h||',['N^{' num2str(r3) '}'], 'LOCATION','Best');
end % End of SQUAREPOISSON
Data
% load data (right hand side function) function z = f(p) x = p(:,1); y = p(:,2); z = 2*pi^2*cos(pi*x).*cos(pi*y); end % exact solution function z = exactu(p) x = p(:,1); y = p(:,2); z = cos(pi*x).*cos(pi*y) - 1; end % Dirichlet boundary condition function z = g_D(p) z = exactu(p); end % Derivative of the exact solution function z = Du(p) x = p(:,1); y = p(:,2); z(:,1) = -pi*sin(pi*x).*cos(pi*y); z(:,2) = -pi*cos(pi*x).*sin(pi*y); end
| Dof | ||u-u_h|| | ||Du-Du_h|| | ||DuI-Du_h|| |
| 8 | 0.19792794 | 1.5035186 | 0.43962712 |
| 32 | 0.065912866 | 0.8373829 | 0.13223755 |
| 128 | 0.017908413 | 0.43160728 | 0.034847816 |
| 512 | 0.0045763652 | 0.21751113 | 0.0088349807 |
| 2048 | 0.0011504907 | 0.10897223 | 0.0022166851 |
| 8192 | 0.0002880262 | 0.054513305 | 0.00055467254 |
| 32768 | 7.2031833e-05 | 0.027260054 | 0.00013869956 |
Error table
The optimal rate of convergence of the H1-norm (1st order) and L2-norm (2nd order) is observed. The 2nd order convergent rate between two discrete functions |DuI-Duh| is known as superconvergence.