RATE OF CONVERGENCE OF LINEAR FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
This example is to show the rate of convergence of linear finite element approximation of the Poisson equation on the unit square:
for the following boundary condition:
- Non-empty Dirichlet boundary condition.
![$u=g_D \hbox{ on }\Gamma_D, \quad \nabla u\cdot n=g_N \hbox{ on }\Gamma_N. \Gamma _D = \{(x,y): x=0, y\in [0,1]\}, \; \Gamma _N = \partial \Omega \backslash \Gamma _D$](femrateP2_eq34764.png) .
. - Pure Neumann boundary condition.
 .
. - Robin boundary condition.

Contents
clear all; close all; clc; [node,elem] = squaremesh([0,1,0,1],0.25); option.L0 = 1; option.maxIt = 4; option.printlevel = 1; option.plotflag = 0; option.elemType = 'P2'; format shorte
Non-empty Dirichlet boundary condition.
pde = sincosdata; bdFlag = setboundary(node,elem,'Dirichlet','~(x==0)','Neumann','x==0'); err = femPoisson(node,elem,pde,bdFlag,option);
Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method #dof: 4225, #nnz: 39184, iter: 10, err = 2.6755e-09, time = 0.52 s Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method #dof: 16641, #nnz: 160272, iter: 10, err = 5.4569e-09, time = 0.51 s
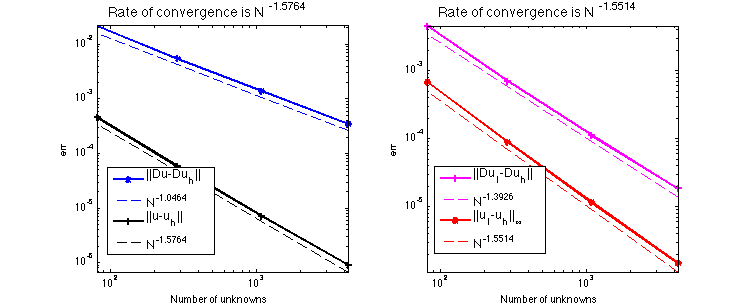
display(' ||u-u_h|| ||Du-Du_h|| ||DuI-Du_h|| ||uI-u_h||_{max}');
display([err.L2 err.H1 err.uIuhH1 err.uIuhMax]);
||u-u_h|| ||Du-Du_h|| ||DuI-Du_h|| ||uI-u_h||_{max}
ans =
4.5722e-04 2.1682e-02 4.5133e-03 6.7421e-04
5.7049e-05 5.4875e-03 6.9756e-04 8.8853e-05
7.1342e-06 1.3779e-03 1.1074e-04 1.1453e-05
8.9219e-07 3.4505e-04 1.8246e-05 1.4548e-06
Pure Neumann boundary condition.
pde = sincosNeumanndata;
bdFlag = setboundary(node,elem,'Neumann');
err = femPoisson(node,elem,pde,bdFlag,option);
Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method #dof: 4225, #nnz: 41458, iter: 10, err = 5.8429e-09, time = 0.53 s Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method #dof: 16641, #nnz: 164850, iter: 11, err = 3.9313e-09, time = 1.3 s
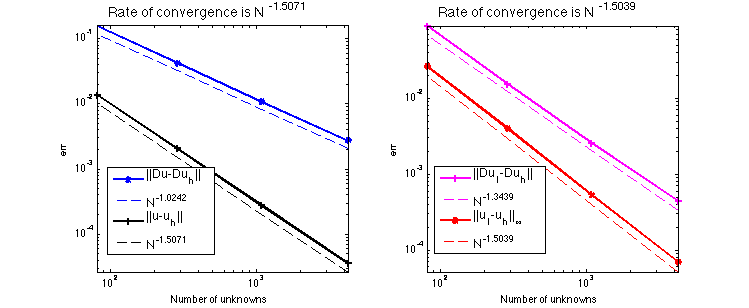
display(' ||u-u_h|| ||Du-Du_h|| ||DuI-Du_h|| ||uI-u_h||_{max}');
display([err.L2 err.H1 err.uIuhH1 err.uIuhMax]);
||u-u_h|| ||Du-Du_h|| ||DuI-Du_h|| ||uI-u_h||_{max}
ans =
1.3592e-02 1.5713e-01 8.9370e-02 2.6274e-02
2.0398e-03 4.2201e-02 1.5150e-02 3.9808e-03
2.7330e-04 1.0834e-02 2.5578e-03 5.3478e-04
3.5211e-05 2.7383e-03 4.3864e-04 6.8974e-05
Pure Robin boundary condition.
option.plotflag = 0;
pdeRobin = sincosRobindata;
bdFlag = setboundary(node,elem,'Robin');
err = femPoisson(node,elem,pdeRobin,bdFlag,option);
Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method #dof: 4225, #nnz: 41473, iter: 9, err = 8.3083e-09, time = 1.1 s Multigrid V-cycle Preconditioner with Conjugate Gradient Method #dof: 16641, #nnz: 164865, iter: 10, err = 2.5881e-09, time = 0.98 s
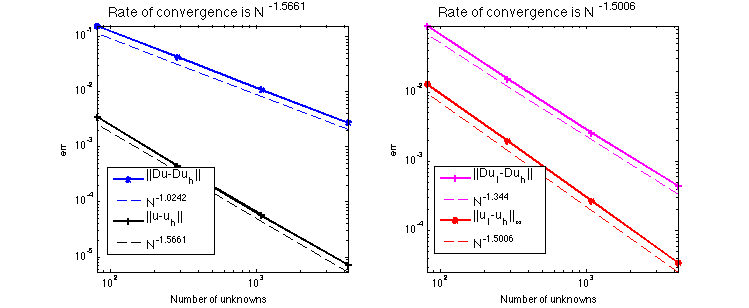
display(' ||u-u_h|| ||Du-Du_h|| ||DuI-Du_h|| ||uI-u_h||_{max}');
display([err.L2 err.H1 err.uIuhH1 err.uIuhMax]);
||u-u_h|| ||Du-Du_h|| ||DuI-Du_h|| ||uI-u_h||_{max}
ans =
3.4930e-03 1.5715e-01 8.9472e-02 1.2867e-02
4.4650e-04 4.2204e-02 1.5165e-02 1.9596e-03
5.6508e-05 1.0834e-02 2.5598e-03 2.6443e-04
7.1046e-06 2.7384e-03 4.3889e-04 3.4231e-05
Conclusion
The optimal rate of convergence of the H1-norm (2nd order) and L2-norm (3rd order) is observed. The order of |DuI-Duh| is almost 3rd order and thus superconvergence exists.
MGCG converges uniformly in all cases.